Soils and Soil types
What is soil?
Soil is:
- One of the basic resources we need to survive – like air and water
- The surface layer of the Earth that contains all the nutrients plants need to grow. The quality of a soil determines what can grow there.
- Home to many plants, animals, and other organisms like bacteria
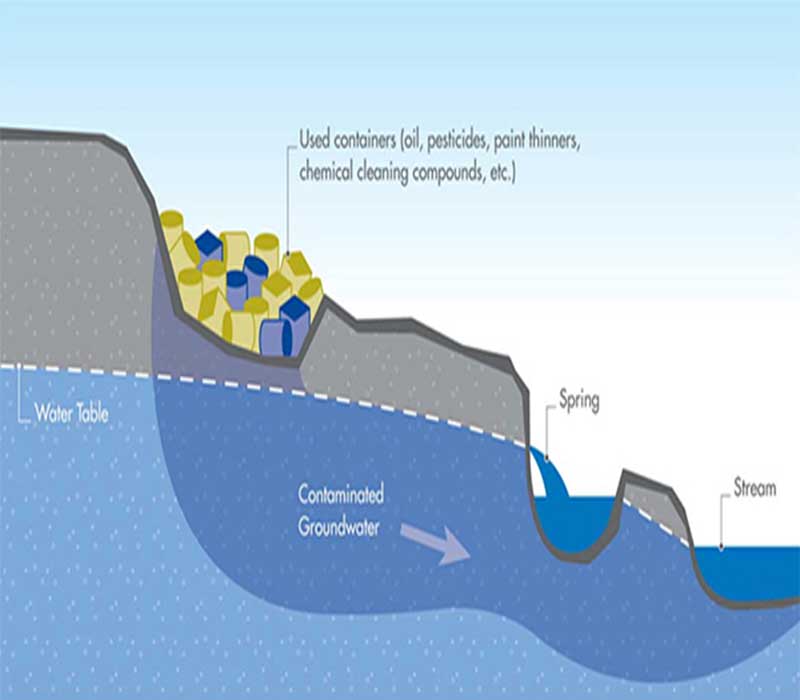
- An important filter of water and wastes.

What is soil made of?
Soil is made up of:
- Broken particles of rock and minerals that have been eroded from rock and changed by the physical and chemical processes of weathering.
- Organic material including living organisms, dead plants and animals, and decomposed plant remains called Humus , Air and Water
How do we describe soils?
Texture – the size of the rock and mineral bits in the soil determines the texture.
- Gravel – pieces larger than 2 mm
- Sand – pieces between 0.05 mm and 2 mm – feels ‘gritty’
- Silt – pieces between 0.002 mm and 0.05 mm – feels like flour
- Clay – pieces smaller than 0.002 mm — feels sticky when wet
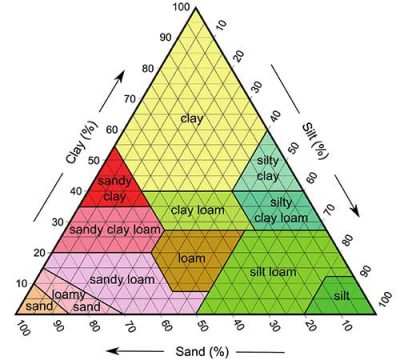
Soil Triangle
There are three basic types of soil: sand, silt and clay. But, most soils are composed of a combination of the different types. How they mix will determine the texture of the soil, or, in other words, how the soil looks and feels.
Soil can be categorised into sand, clay, silt, peat, chalk and loam types of soil based on the dominating size of the particles within a soil.

Soil Texture
Why does soil texture matter?
Too much sand and gravel – create big spaces between the pieces of soil that don’t hold water or nutrients for plants. Plants can’t grow well. Too much silt – makes good farm land but erodes away easily – is picked up and carried away during floods and blows away during dust storms. Too much clay – makes the soil heavy and dense – not enough space between the tiny particles makes the soil almost like concrete when it’s dry. Plants can’t get air, nutrients, or water and can’t grow. Loamis the perfect soil. It has equal amounts of sand and silt and a smaller amount of clay. It has enough space between soil pieces for water and air to flow and enough clay to stick together and hold in nutrients. Chalk soils can be either light or heavy but always highly alkaline due to the calcium carbonate or lime within its structure. As these soils are alkaline they will not support the growth of plants that require acidic soils to grow. If a chalky soil shows signs of visible white lumps then they can’t be acidified and gardeners should be resigned to only choose plants that prefer an alkaline soil.

Clay soil

sandy soil

Silt Soil

Loamy Soil

Peat Soil

Chalk Soil
What factors determine a soil’s texture & composition?
Different soil types develop in different climates due to:
- Bedrock type
- Amount of precipitation (rainfall)
- Temperature
- Time
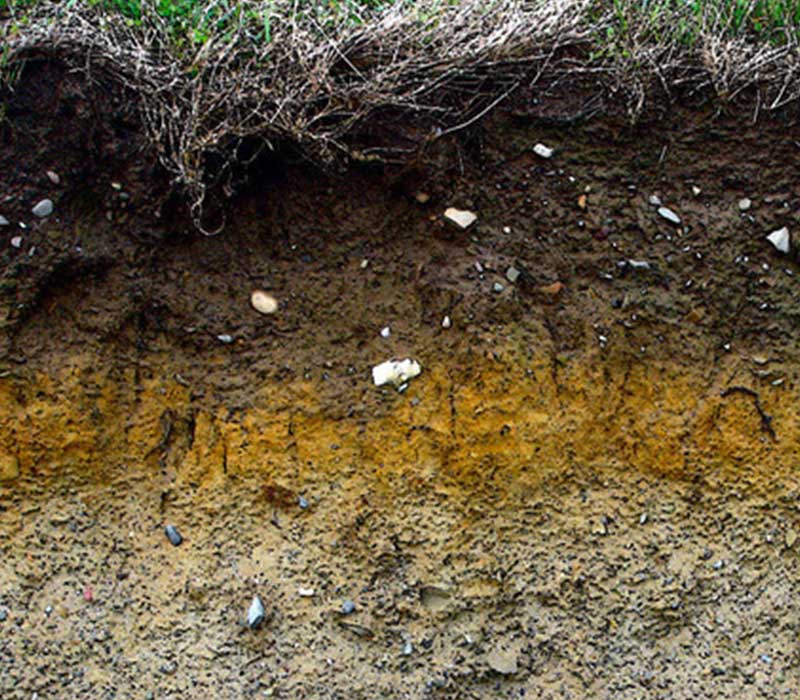
How is soil structured?
Soil forms in layers that we call horizons:
- O-horizon – organic matter, dead leaves, plant & animal matter
- A-horizon – “topsoil” – mineral soil with nutrients. Most plants root here.
- E-horizon – leaching zone (caliche)
- B-horizon – “subsoil” – mineral particles, clays, salts
- C-horizon – weathered & broken parent tock
- D-Horizon – “bedrock” – solid parent rock

Types of soil in different climatic regions of the world

Prairie soils — dark A-horizon, rich in minerals, form in mid-latitudes & support grasslands Soils.

Forest soils — light gray A-horizon, rich in Al & Fe, This soil are found in temperate humid regions of the world

Desert soils — very thin (a few cm), little organic material, rich in CaCO3 nodules & layers (caliche), form in deserts Soils-4-6

Tropical soils — reddish and iron-oxide rich, nutrients are leached out, form in humid & warm regions.

Tundra Soil
Tundra soils – Arctic & Antarctic and in high elevations, bottom layers always frozen (permafrost), very fragile – take thousands of years to form and recover from damage.